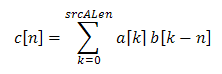|
| void | tpt_correlate_f32 (f32_t *aOutData, const f32_t *aInDataA, uint32_t aLenA, const f32_t *aInDataB, uint32_t aLenB) |
| | Correlation of floating-point sequences. More...
|
| |
| tpt_status | tpt_correlate_fast_f32 (f32_t *aOutData, const f32_t *aInDataA, uint32_t aLenA, const f32_t *aInDataB, uint32_t aLenB) |
| | Correlation of floating-point sequences (fast version). More...
|
| |
| void | tpt_correlate_q15 (q15_t *aOutData, const q15_t *aInDataA, uint32_t aLenA, const q15_t *aInDataB, uint32_t aLenB) |
| | Correlation of Q15 sequences. More...
|
| |
| void | tpt_correlate_q31 (q31_t *aOutData, const q31_t *aInDataA, uint32_t aLenA, const q31_t *aInDataB, uint32_t aLenB) |
| | Correlation of Q31 sequences. More...
|
| |
| void | tpt_correlate_q7 (q7_t *aOutData, const q7_t *aInDataA, uint32_t aLenA, const q7_t *aInDataB, uint32_t aLenB) |
| | Correlation of Q7 sequences. More...
|
| |
Correlation is a mathematical operation that is similar to convolution. As with convolution, correlation uses two signals to produce a third signal. The underlying algorithms in correlation and convolution are identical except that one of the inputs is flipped in convolution. Correlation is commonly used to measure the similarity between two signals. It has applications in pattern recognition, cryptanalysis, and searching. The DSP library provides correlation functions for Q15, Q31 and floating-point data types. Fast versions of the floating-point functions are also provided.
- Algorithm
- Let
a[n] and b[n] be sequences of length aLenA and aLenB samples respectively. The convolution of the two signals is denoted by
c[n] = a[n] * b[n]
In correlation, one of the signals is flipped in time
c[n] = a[n] * b[-n]
- and this is mathematically defined as
- The
aInDataA points to the first input vector of length aLenA and aInDataB points to the second input vector of length aLenB. The result c[n] is of length 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1 and is defined over the interval n = 0, 1, 2, ..., (2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 2). The output result is written to aOutData and the calling function must allocate 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1 words for the result.
- Note
- The
aOutData should be initialized to all zeros before being used.
- Fixed-Point Behavior
- Correlation requires summing up a large number of intermediate products. As such, the Q15, and Q31 functions run a risk of overflow and saturation. Refer to the function specific documentation below for further details of the particular algorithm used.
- Fast Versions
- Fast versions are supported for floating-point. Time complexity for Fast versions are less compared to floating-point of conv and the design consumes more memory.
◆ tpt_correlate_f32()
| void tpt_correlate_f32 |
( |
f32_t * |
aOutData, |
|
|
const f32_t * |
aInDataA, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenA, |
|
|
const f32_t * |
aInDataB, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenB |
|
) |
| |
Correlation of floating-point sequences.
- Parameters
-
| [out] | aOutData | points to the location where the output result is written. Length 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1. |
| [in] | aInDataA | points to the first input sequence |
| [in] | aLenA | length of the first input sequence |
| [in] | aInDataB | points to the second input sequence |
| [in] | aLenB | length of the second input sequence |
- Returns
- none
◆ tpt_correlate_fast_f32()
| tpt_status tpt_correlate_fast_f32 |
( |
f32_t * |
aOutData, |
|
|
const f32_t * |
aInDataA, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenA, |
|
|
const f32_t * |
aInDataB, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenB |
|
) |
| |
Correlation of floating-point sequences (fast version).
- Parameters
-
| [out] | aOutData | points to the location where the output result is written. Length 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1. |
| [in] | aInDataA | points to the first input sequence. |
| [in] | aLenA | length of the first input sequence |
| [in] | aInDataB | points to the second input sequence. |
| [in] | aLenB | length of the second input sequence |
- Returns
- execution status
◆ tpt_correlate_q15()
| void tpt_correlate_q15 |
( |
q15_t * |
aOutData, |
|
|
const q15_t * |
aInDataA, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenA, |
|
|
const q15_t * |
aInDataB, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenB |
|
) |
| |
Correlation of Q15 sequences.
- Parameters
-
| [out] | aOutData | points to the location where the output result is written. Length 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1. |
| [in] | aInDataA | points to the first input sequence |
| [in] | aLenA | length of the first input sequence |
| [in] | aInDataB | points to the second input sequence |
| [in] | aLenB | length of the second input sequence |
- Returns
- none
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- The function is implemented using a 64-bit internal accumulator. Both inputs are in 1.15 format and multiplications yield a 2.30 result. The 2.30 intermediate results are accumulated in a 64-bit accumulator in 34.30 format. This approach provides 33 guard bits and there is no risk of overflow. The 34.30 result is then truncated to 34.15 format by discarding the low 15 bits and then saturated to 1.15 format.
◆ tpt_correlate_q31()
| void tpt_correlate_q31 |
( |
q31_t * |
aOutData, |
|
|
const q31_t * |
aInDataA, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenA, |
|
|
const q31_t * |
aInDataB, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenB |
|
) |
| |
Correlation of Q31 sequences.
- Parameters
-
| [out] | aOutData | points to the location where the output result is written. Length 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1. |
| [in] | aInDataA | points to the first input sequence. |
| [in] | aLenA | length of the first input sequence |
| [in] | aInDataB | points to the second input sequence. |
| [in] | aLenB | length of the second input sequence |
- Returns
- none
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- The function is implemented using an internal 64-bit accumulator. The accumulator has a 2.62 format and maintains full precision of the intermediate multiplication results but provides only a single guard bit. There is no saturation on intermediate additions. Thus, if the accumulator overflows it wraps around and distorts the result. The input signals should be scaled down to avoid intermediate overflows. Scale down one of the inputs by 1 / min(aLenA, aLenB) to avoid overflows since a maximum of min(aLenA, aLenB) number of additions is carried internally. The 2.62 accumulator is right shifted by 31 bits and saturated to 1.31 format to yield the final result.
◆ tpt_correlate_q7()
| void tpt_correlate_q7 |
( |
q7_t * |
aOutData, |
|
|
const q7_t * |
aInDataA, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenA, |
|
|
const q7_t * |
aInDataB, |
|
|
uint32_t |
aLenB |
|
) |
| |
Correlation of Q7 sequences.
Correlation of Q15 sequences.
- Parameters
-
| [out] | aOutData | points to the location where the output result is written. Length 2 * max(aLenA, aLenB) - 1. |
| [in] | aInDataA | points to the first input sequence |
| [in] | aLenA | length of the first input sequence |
| [in] | aInDataB | points to the second input sequence |
| [in] | aLenB | length of the second input sequence |
- Returns
- none
- Scaling and Overflow Behavior
- The function is implemented using a 32-bit internal accumulator. Both inputs are in 1.7 format and multiplications yield a 2.14 result. The 2.14 intermediate results are accumulated in a 64-bit accumulator in 18.14 format. This approach provides 17 guard bits and there is no risk of overflow. The 18.14 result is then truncated to 18.7 format by discarding the low 7 bits and then saturated to 1.7 format.