 |
LIBML
Version 3.2.4
LIBML DSP Software Library
|
 |
LIBML
Version 3.2.4
LIBML DSP Software Library
|
Functions | |
| static void | tpt_inv_clarke_f32 (f32_t *pIa, f32_t *pIb, f32_t Ialpha, f32_t Ibeta) |
| Floating-point Inverse Clarke transform. More... | |
| static void | tpt_inv_clarke_q31 (q31_t *pIa, q31_t *pIb, q31_t Ialpha, q31_t Ibeta) |
| Inverse Clarke transform for Q31 version. More... | |
Inverse Clarke transform converts the two-coordinate time invariant vector into instantaneous stator phases.
The function operates on a single sample of data and each call to the function returns the processed output. The library provides separate functions for Q31 and floating-point data types.
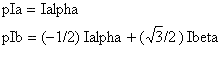
pIa and pIb are the instantaneous stator phases and Ialpha and Ibeta are the two coordinates of time invariant vector. Floating-point Inverse Clarke transform.
| [out] | pIa | points to output three-phase coordinate a. |
| [out] | pIb | points to output three-phase coordinate b. |
| [in] | Ialpha | input two-phase orthogonal vector axis alpha |
| [in] | Ibeta | input two-phase orthogonal vector axis beta |
Inverse Clarke transform for Q31 version.
| [out] | pIa | points to output three-phase coordinate a. |
| [out] | pIb | points to output three-phase coordinate b. |
| [in] | Ialpha | input two-phase orthogonal vector axis alpha |
| [in] | Ibeta | input two-phase orthogonal vector axis beta |